8 Focused Assessment- HEENT
Learning Objectives
At the end of this chapter, the learner will:
- Obtain a health history related to the head, eyes, ears, nose and throat (HEENT).
- Perform a physical assessment of the body systems that make up HEENT using correct techniques.
- Document findings of the HEENT and neck exam.
I. Overview of the Head, Eyes, Ears, Nose, and Throat (HEENT)
The assessment of the HEENT systems will include examinations of the head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat/neck. The HEENT examination will include assessing the HEENT for symmetry, and color; hair distribution to scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes; hydration status of the mucus membranes to the nose and mouth; the number and condition of teeth, palate structure and uvula placement and color of lips and buccal membrane. Included in the assessment are the XII cranial nerves.
The examination of the HEENT systems will be completed by inspecting and palpating the head, eyes, ears, nose, throat/neck, lymph nodes, and testing the cranial nerves that innervate the function of each organ/structure of HEENT.
II. Anatomy and Physiology
Click the links below to review anatomy and physiology of the HEENT system. In the assessment process, you will need to apply your knowledge of the A & P to the HEENT system.
Watch and learn from the following videos:
Please use this link if the Youtube is not visible Landmarks of the Head and Neck
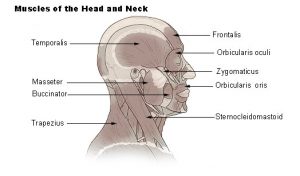
Anatomy of the muscle of the Head and the Neck. If the picture is not visible click the link: https://psychology.wikia.org/wiki/Zygomaticus_major_muscle
If the picture below is not visible click on the link: Structures and functions of the eyes

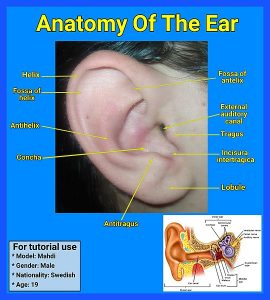
Anatomy of the Ear: If the picture below is not visible click on the link: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anatomy_of_the_ear.jpg
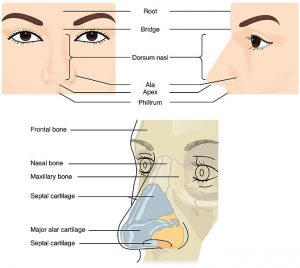
If the picture below is not visible then click on this link: Anatomy of the Nose
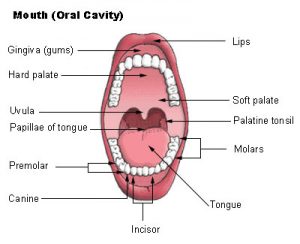
Anatomy of the Oral cavity If the picture is not visible click on this link: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mouth_assessment
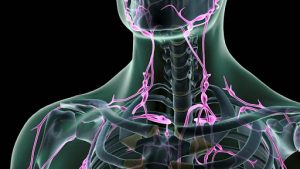
Anatomy of the Lymph Nodes to the Head and Neck if the picture is not visible click the link: https://medika.life/the-lymph-nodes/
Cranial Nerve Function-This is discussed in more detail in the Neurological chapter.
|
Number
|
Mnemonic
|
Cranial Nerve
|
Function (S/M/B)
|
Mnemonic
|
|
I |
On |
Olfactory |
Smell (S) |
Some |
|
II |
On |
Optic |
Vision (S) |
Say |
|
III |
On |
Oculomotor |
Eye Movements (M) |
Marry |
|
IV |
They |
Trochlear |
Eye Movements (M) |
Money |
|
V |
Traveled |
Trigeminal |
Sensory/motor – face (B) |
But |
|
VI |
And |
Abducens |
Eye movements (M) |
My |
|
VII |
Found |
Facial |
Motor-face, Taste (B) |
Brother |
|
VIII |
Voldemort |
Vestibulocochlear (Auditory) |
Hearing/Balance (S) |
Says |
|
IX |
Guarding |
Glossopharyngeal |
Motor – throat Taste (B) |
Big |
|
X |
Very |
Vagus |
Motor/sensory – viscera (autonomic) (B) |
Bucks |
|
XI |
Ancient |
Accessory |
Motor-head &neck (M) |
Mean |
|
XII |
Horcruxes |
Hypoglossal |
Motor-lower throat (M) |
More |
Knowledge Check
III. Related Medical Terminology
| Accommodation | The eye’s lens’ ability to change shape in order to focus from distant to near or near to distant |
| Amblyopia | Decrease vision to one eye only. Also called a lazy eye |
| Astigmatism | There is a deviation in the curvature of the eye’s lens or cornea leading to distorted or blurry |
| Auricle | The visible part of the auditory system also called the pinna or the ear |
| Blepharitis | Bilateral Inflammation along the edges of the eyelids |
| Buccal | Associated with the cheek |
| Candidiasis (Thrush) | Candida is a yeast that causes a fungal infection to the mouth, throat, gut, vagina, and skin |
| Canthus | “The angle or corner on each side of the eye, formed by the junction of the upper and lower lids.” |
| Cataract | The clouding of the eye’s Len causes blurred vision |
| Cerumen | Glands in the ear canal produce ear wax also called cerumen |
| Conjunctivitis | Infection of the transparent membrane lining the outer layer of the eyelid and eyeball- Pink eyes |
| Diplopia | An individual sees two images of the same thing also called Double vision |
| Tonsillar exudate | Tonsils secrete fluid in response to an infection to the tonsils itself |
| Frenulum of the tongue | A folded piece of tissue that connects the posterior center of the tongue to the mouth |
| Glaucoma | Abnormally high pressure in the eyes damages the optic nerve which can lead to blindness. |
| Gingivitis | “Mild and common gum disease.” |
| Glossitis | Inflammation of the tongue. |
| Myopia | Close objects are seen better than distant objects. |
| Normocephalic | Normal size and shape of the head that is age-appropriate |
| Occipital | Relate to or located to the back of the head |
| Oropharynx | Includes the soft palate, side and back wall of the throat, tonsils, and back third of the tongue |
| Otorrhea | Ear drainage/discharge |
| Periodontitis | Gum disease |
| Photophobia | Light sensitivity |
| Presbycusis | Hearing loss mostly from aging |
| Ptosis | Drooping of the eyelid |
| Rhinorrhea | Excessive nasal drainage-runny nose discharge |
| Sclera | The tough white outer coat covering approx. 5/6 of the posterior surface of the eyeball |
| Strabismus | At least one eye muscle is weak causing the eyes not to line up in the same direction. |
| Tinnitus | Ringing or other abnormal noises in one or both of your ears. |
| Xerostomia | Dry mouth from a deficit of saliva production. |
Knowlege Check
IV. Step by Step Assessment
- Perform hand hygiene.
- Check room for contact precautions.
- Introduce yourself to the patient.
- Confirm patient ID using two patient identifiers (e.g., name and date of birth).
- Explain the process to the patient.
- Assemble equipment prior to starting the exam.
- Be organized and systematic in your assessment.
- Use appropriate listening and questioning skills.
- Listen and attend to patient cues.
- Ensure patient’s privacy and dignity.
- Apply principles of asepsis and safety.
- Check vital signs.
HEENT Exam
| Steps |
Additional Information |
| 1. Conduct a focused interview related to HEENT and related diseases. | Ask relevant questions related to:
pain to the head, eyes, ear, nose, throat and neck or drainage as applicable. about changes to sight, smell, hearing, taste, chewing, swallowing and speech. the need for glasses, hearing aids, dentures. acute or chronic disease of the HEENT and medication used to treat mentioned disease or abnormalities. risk factors noted to the HEENT systems. |
| 2. Inspect: | Head
Eyes
Ears
Nose and Paranasal Sinuses
Mouth
|
| 3. Tests for assessment of the eys | Pupillary reaction to light
https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/phys-2019-0047/html Test pupil reaction directly and consensually Test extraocular movements (CN III, IV, VI) while stabilizing the head so that all nine cardinal gazes are tested: If the picture is not visible click on the link: https://youtu.be/GeQZlxACBY0
If the picture is not visible click on the link: https://www.drawittoknowit.com/course/neuroanatomy/glossary/physical-exam/cardinal-positions-of-gaze Test for convergence by moving finger toward the bridge of the nose
|
| Palpate/Tests to assess the ears | https://youtu.be/ixOj-RkoxNA
If gross hearing test is abnormal, then perform the following optional tests:
|
| Palpate/Tests to assess the Nose |
|
| Palpate/Tests to assess the Mouth |
If the youtube above is not visible click on this link: https://youtu.be/gmJxLhCpCQw
|
| Neck
Palpate/Tests to assess the Neck
|
Neck and Lymph node assessment should include:
Thyroid examination: If the picture below is not visible click on this link: https://youtu.be/RfmO9k9neWM-this is actually a Youtube. Examine thyroid gland 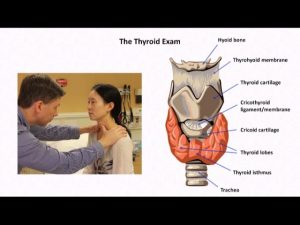 Lymph node examination
|
| HEENT exam | If the youtube is not visible please click on this link: https://youtu.be/MkqCjH-BlMo |
V. Documentation of Assessment Findings
A sample of the narrative documentation:
The Head is normacephalic and without lesions or bumps. Hair is thick and curly without patches or ball spots and the scalp is clean. The face is symmetrical and smooth. Temporal pulse is palpable at 2/5 bilaterally.
Eyes are distantly placed and equal in size and shape with thick black eyelashes. Eyebrows are thick but tapered and well kept. Eyelids in normal position with no abnormal widening or ptosis. No redness, discharge, or crusting was noted on lid margins. Conjunctiva and sclera appear moist and smooth. Sclera white with no lesions or redness. No swelling or redness over the lacrimal gland. The cornea is transparent, smooth, and moist with no opacities, the lens is free of opacities. Irises are round, flat, and evenly colored brown. Pupils are equal in size and reactive to light and accommodation. Pupils converge evenly. Extraocular movements were smooth and symmetric in all nine cardinal gazes with no nystagmus. Vision is 20/20 via the Snellen Chart.
Ears are equal in size bilaterally. Auricles are aligned with the corner of each eye. Skin smooth, no lumps, lesions, nodules. No discharge. Nontender on palpation. A small amount of moist yellow cerumen in the external canal. Whisper test: patient repeats 2 syllable words.
Lips pink, smooth, and moist without lesions. The buccal mucosa is pink, moist, and without exudates. Thirty-two white to yellowish teeth are present with no cavities noted. Gums pink without redness or swelling. The tongue protrudes to a normal distance without tremors, is midline, and is equal bilateral in strength. Ventral surface of tongue smooth and shiny pink with small visible veins present. Frenulum in the midline. Soft palate smooth and pink. Tonsillar pillars are pink and symmetric and Uvula is midline.
The nose is normal size but smooth, symmetric, and midline. Each nare is patent. The nasal septum slightly deviated to the left but does not obstruct airflow. Inferior and middle turbinates are dark pink, moist, and free of lesions. No purulent drainage was noted. Frontal and Maxillary sinuses are non-tender upon palpation. The temporomandibular joint has full range of motion without tenderness or crepitus. Cranial Nerves II-XII are grossly intact.
Neck symmetric with centered head position and no bulging masses. C7 is visible and palpable with neck flexion. Has smooth, controlled, full range of motion of the neck. Thyroid gland nonvisible but palpable when swallowing. Trachea in the midline. Lymph nodes are nonpalpable.
VI. Related Laboratory and Diagnostic Procedures/Findings
CBC-complete blood count
BMP-Basic Metabolic Panel
Lipid panel including Total cholesterol. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol, Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and Triglycerides.
https://www.revieweducationgroup.com/ce/the-when-and-why-of-ordering-blood-work
Ear drainage culture https://www.ucsfhealth.org/medical-tests/ear-drainage-culture
Bleeding time: Pt, PTT, and INR.
CT Scan of the head/brain.
Direct laryngoscopy and Videostroboscopy. https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/laryngeal-and-hypopharyngeal-cancer/diagnosis
A more detailed overview of putting the HEENT assessment together is seen on the following website: https://nextgencombatmedic.com/2017/04/06/neurological-assessment/
VII. Learning Exercises
After watching the HEENT assessment video above complete the following exercises:
VII. Citation and Attribution:
Daniel M, Rougas S, Warrier S, Tabaddor R, Bray K, Taylor J. Teaching physical exam skills to novices: developing all the tools in the clinician toolbox. MedEdPORTAL. 2015;11:10057. https://doi.org/10.15766/mep_2374-8265.10057
Swift, Heather ( 2013). Charting example for physical assessment. https://othersideofthestethoscope.wordpress.com/2013/10/24/charting-examples-for-physical-assessment/
US National Library of Medicine. https://medlineplus.gov/
Surface anatomy landmarks of the head and neck (preview)Human anatomy Kenhub, January 31, 2019, Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license. Retrieved 20:08 July 27, 2021, https://youtu.be/b6O-TrwFor0
Main Muscles of the Head and Neck (preview)-Human Anatomy-Kenhub, January 27, 2020 Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license, Retrieved 20:08 July 27, 2021 https://youtu.be/lkt-8XcpHr0
Anatomy and Physiology-Sensory System. The eye, March 31, 2015 Creative Common, Retrieved 20:40 July 27, 2021 https://youtu.be/e0KmUctCErI
Anatomy of the Human Ear. June 25, 2016 Creative Common, Retrieved 20:40 July 27, 2021, https://youtu.be/3G5jiXl2LSM
The lymph nodes-Medika life: Understanding Human Anatomy Updated July 22, 2020, Retrieved 23:40 July 27, 2021, https://medika.life/the-lymph-nodes/
File: Anatomy of the ear.jpg Wikimedia commons Uploaded December 2, 2020 Retrieved 24:21 July 28, 2021 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Anatomy_of_the_ear.jpg
Douglas College Human Anatomy and Physiology (1st ED.) BC CAmpus 11.3 Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back Retrieved 01:21 July 7-28-2021, https://pressbooks.bccampus.ca/dcbiol11031109/chapter/11-3-axial-muscles-of-the-head-neck-and-back/
Zygomaticus major muscle-Psychology Wiki-Fandom, Muscle of the Head and Neck Retrieved 01:27 July 28, 2021 https://psychology.wikia.org/wiki/Zygomaticus_major_muscle
Clinical Examination of the Musculoskeletal system. Open Library Pressbooks Cranial Nerves. Retrieved 01:27 July 28, 2021 https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/clinicalexamination/chapter/neurological-assessment/
Mouth exam -ENT Oxford Department of ENT February 17, 2012, Retrieved July 28, 2021, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gmJxLhCpCQw
The Thyroid Exam and Physical Diagnosis of Thyroid Disease November 6, 2014, Retrieved July 28, 2021, https://youtu.be/RfmO9k9neWM