4.2. Interpreting data (Reading)
Learning Objectives
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
- Identify and interpret healthcare-related data in written and visual formats.
- Communicate health data effectively to patients using clear, simple language.
- Identify key data points in healthcare materials such as articles, charts, graphs, and tables.
- Analyze and interpret healthcare data, understanding its implications for patient care.
- Practice communicating data to patients through role-play scenarios.
- Reflect on the importance of data interpretation in their roles as future healthcare professionals.
Part 1: Warm-Up
Discussion
- Why is it essential to understand data when interacting with patients?
- Can you think of a time when data helped a doctor or CMA make a decision?
- How can misunderstanding data affect patient care?
Part 2: Understanding Healthcare Data
Materials: Short article about healthcare data (e.g., interpreting blood pressure readings, survey results)
Distribute the article handout.
In pairs, students:
- Read the article “Understanding Healthcare Data.”
- Underline or highlight key data points (numbers, percentages, trends).
- Discuss: What does this data mean? Why is it important?
Each pair shares one significant data point and its implication with the class.
Part 3: Reading
Read the article below and answer the following comprehension Questions
- What is the main topic of the article?
- What type of data is included?
- How does this data impact patient care?
- Why is it important for a CMA to understand this information?
Understanding Healthcare Data
In healthcare, data helps providers understand a patient’s condition and make good decisions. For example, blood pressure is a common number used in healthcare. A normal reading is around 120/80 mmHg. If a patient’s reading is 140/90 mmHg or higher, this can be a sign of high blood pressure. This condition needs attention because it increases the risk of heart problems.
Healthcare workers also use temperature, pulse, and oxygen saturation as vital data points. For instance, a temperature over 100.4°F may show signs of a fever or infection. An oxygen saturation level below 95% may indicate breathing issues and should be closely monitored, especially in elderly patients or those with respiratory conditions.
Another type of data healthcare workers study is patient feedback. Clinics and hospitals often conduct patient satisfaction surveys. For example, a survey might show that 85% of patients feel they were treated with respect, while only 60% say they clearly understood their discharge instructions. This tells the clinic they are doing a good job with respectful care but need to improve communication about follow-up instructions.
Sometimes, clinics look at data over time to identify trends. If missed appointments have increased from 10% to 20% over six months, it may suggest scheduling problems or transportation issues in the community. Addressing this can lead to better access and outcomes for patients.
When CMAs and other healthcare workers understand and use data, they can help improve patient care and safety. They are also better able to communicate with the healthcare team and support patients more effectively.
Part 4: Analyzing Healthcare Data
In small groups, review the charts, graphs, and tables provided below. Use the table below to organize your analysis:
| Data Type | Key Trends Observed | What Does This Suggest About Patient Care? |
|---|---|---|
| Example: Patient Satisfaction Survey | 80% of patients rated their care as “Excellent” | Suggests high-quality care but room for improving the 20% |
Chart: Patient Blood Pressure Readings Over Time
Chart Title: Blood Pressure Readings for Patient Over 3 Weeks
(Normal blood pressure range is 120/80 mmHg)
| Date | Systolic (mmHg) | Diastolic (mmHg) | Notes |
| Week 1: April 1 | 140 | 90 | Elevated, patient reported stress |
| Week 2: April 8 | 135 | 85 | Slight improvement |
| Week 3: April 15 | 130 | 80 | Near normal, patient increased exercise |
|---|
Graph : Patient Satisfaction Survey Results
Graph Title: Patient Satisfaction with Healthcare Services
(Based on a survey of 100 patients)
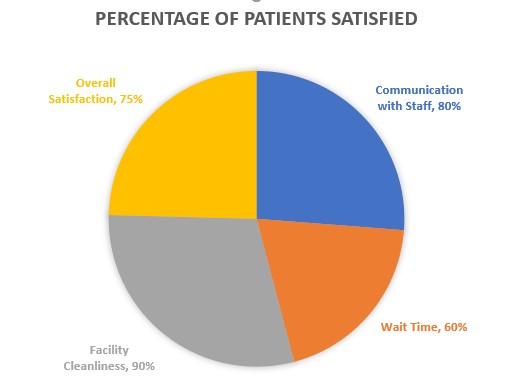
Table : Trend in Flu Vaccination Rates
Table Title: Flu Vaccination Rates Over 3 Years
(Reported for Clinic Patients Aged 18+)
| Year | Number of Patients Vaccinated | Percentage of Total Patients |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 | 2,000 | 50% |
| 2023 | 2,500 | 62.5% |
| 2024 | 3,000 | 75% |
Part 5: Communicating Data to Patients
Your group will be assigned to one of the below role-play card with a specific scenario involving healthcare data.
Identify the key data points you’ll discuss with the patient.
Plan how to explain the data in simple, clear, and patient-friendly language.
Practice using a professional and empathetic tone.
Use the space below to plan your role-play:
Scenario: _________________________________________________________________________
Key Data Points to Discuss: ___________________________________________________________
How Will You Explain the Data to the Patient? ____________________________________________
Scenario 1: Explaining Blood Pressure Readings
Background: You are a Certified Medical Assistant (CMA) speaking with a patient named Maria who has been monitoring her blood pressure. During her last appointment, her readings were elevated.
Patient Information:
- Name: Maria Lopez
- Age: 45
- Recent Blood Pressure Readings: 150/95 mmHg (normal range is 120/80 mmHg)
Instructions:
- Explain to Maria what her blood pressure readings mean.
- Discuss the potential health risks associated with high blood pressure (hypertension).
- Provide recommendations for lifestyle changes (e.g., diet, exercise) and the importance of follow-up appointments.
Key Points to Communicate:
- What the numbers mean (systolic vs. diastolic).
- The implications of her readings on her health.
- Suggested next steps for managing her blood pressure.
Scenario 2: Discussing Cholesterol Test Results
Background: You are a CMA discussing cholesterol test results with a patient named John who has been concerned about his heart health.
Patient Information:
- Name: John Smith
- Age: 50
- Cholesterol Test Results:
- Total Cholesterol: 240 mg/dL (normal <200 mg/dL)
- LDL (bad cholesterol): 160 mg/dL (normal <100 mg/dL)
- HDL (good cholesterol): 40 mg/dL (normal >60 mg/dL)
Instructions:
- Explain John’s cholesterol results, particularly the significance of high total cholesterol and LDL levels.
- Discuss the risks associated with high cholesterol, such as heart disease.
- Provide recommendations for dietary changes, exercise, and possible medication.
Key Points to Communicate:
- What the cholesterol numbers indicate about his health.
- The importance of increasing HDL levels and reducing LDL levels.
- Actionable steps John can take to improve his cholesterol.
Scenario 3: Reviewing Patient Satisfaction Survey Results
Background: You are a CMA discussing the results of a patient satisfaction survey with a patient named Lisa who recently visited the clinic.
Patient Information:
- Name: Lisa Chen
- Age: 30
- Survey Results:
- Overall Satisfaction: 75%
- Communication with Staff: 85%
- Wait Time: 60%
- Facility Cleanliness: 90%
Instructions:
- Explain the survey results to Lisa, highlighting areas of strength and areas needing improvement.
- Discuss the importance of patient feedback in improving care quality.
- Encourage Lisa to share her experience and any suggestions for improvement.
Key Points to Communicate:
- What the overall satisfaction percentage means.
- Explain the aspects where patients felt positive (e.g., communication, cleanliness) and where improvements are needed (e.g., wait time).
- Invite Lisa to provide her feedback and how it can help enhance the clinic services.
Part 6: Wrap-Up and Reflection
Wrap-Up and Reflection
Whole class discuss:
- What did you learn today about interpreting healthcare data?
- Why is it important to communicate data clearly to patients?
- How can these skills help you as a future CMA?
Reflection:
- One new thing I learned about healthcare data is: ____________
- One challenge I had today was: ____________
- One way I can improve is: ____________
Encourage a few students to share their reflections aloud.
Media Attributions
- Graph module 4

