2.6. Active Reading (Study skill)
Learning Objectives
A the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
- Explain the importance of active reading and note-taking for studying and retaining information, particularly for the CMA exam.
- Identify and apply active reading strategies, such as highlighting and summarizing, to extract key information from study materials.
- Describe and utilize different note-taking methods (Cornell Method, Mind Mapping, Outline Method) to organize information effectively.
- Collaborate with peers to share and evaluate reading and note-taking strategies, gaining insight into their effectiveness.
- Reflect on their learning and set personal goals for incorporating active reading and note-taking into their study routines.
Part 1: Warm-Up: Reflecting on Current Study Habits
Reflect on how you currently read and study. Write your responses to the following questions. Then, share your answers during the class discussion.
- What do you usually do when you read study materials?
- How do you remember key information?
- What challenges do you face when studying?
Discussion
Share your answers to the above questions and the importance of active reading and note-taking in studying for the CMA exam.
Part 2: Applying Active Reading Strategies
Your instructor will explain the two active reading strategies,
- Highlighting: Identifying key terms and concepts while reading.
- Summarizing: Writing brief summaries of sections to capture main ideas.
Read the passage below on Understanding Diabetes Management. While reading, highlight key points, terms, and concepts. After reading, write a short summary (3-5 sentences) of the main ideas.
Reading Passage: Understanding Diabetes Management
Part 3: Note-Taking
Read the three note-taking methods, and tell your partner which method you like to use most.
Note-Taking Methods
Effective note-taking is a crucial skill for students, especially when studying for exams like the CMA. Here are three popular note-taking methods that can help you organize information and enhance your understanding of the material.
1. Cornell Method
The Cornell Method divides your note page into three sections: a narrow left column for cues or questions, a larger right column for detailed notes, and a summary section at the bottom.
Example:
Notes (Right Column): Write down key points from your lecture or reading, such as “Diabetes management includes monitoring blood sugar, diet, and exercise.”
Cues (Left Column): After the lecture, jot down questions or keywords that relate to the notes, like “What are the symptoms of diabetes?”
Summary (Bottom): At the end of your notes, write a brief summary of the main ideas, such as “Effective diabetes management requires a combination of lifestyle changes and regular monitoring.”
This method helps you review and test your understanding later.
2. The Outline Method
The Outline Method organizes information in a structured format using headings and bullet points. This method is great for capturing hierarchical relationships between concepts.
Example:
I. Diabetes Management
A. Monitoring Blood Sugar
- Frequency of checks
- Tools used (e.g., glucometer)
B. Diet
- Foods to include (fruits, vegetables)
- Foods to avoid (sugary snacks)
C. Exercise
- Recommended activities (walking, swimming)
- Frequency (at least 150 minutes per week)
This method allows you to see the main topics and subtopics clearly, making it easier to study.
3. Mind mapping
Mind Mapping is a visual note-taking method that helps you see connections between ideas. You start with a central concept and branch out to related topics.
Example:
Start with “Diabetes Management” in the center of your page.
Draw branches for each main area: “Monitoring,” “Diet,” “Exercise.”
From each branch, add smaller branches with details, such as “Blood Sugar Levels” under “Monitoring” and “Healthy Foods” under “Diet.”
This method is particularly useful for visual learners and helps in brainstorming and organizing thoughts.
Part 4: Practice Note-Taking Techniques
Note-Taking Techniques: Cornell Method
Mind Mapping
The following mind map is about Chapter 22. Read chapter 22, and answer as many questions in 30 minutes.
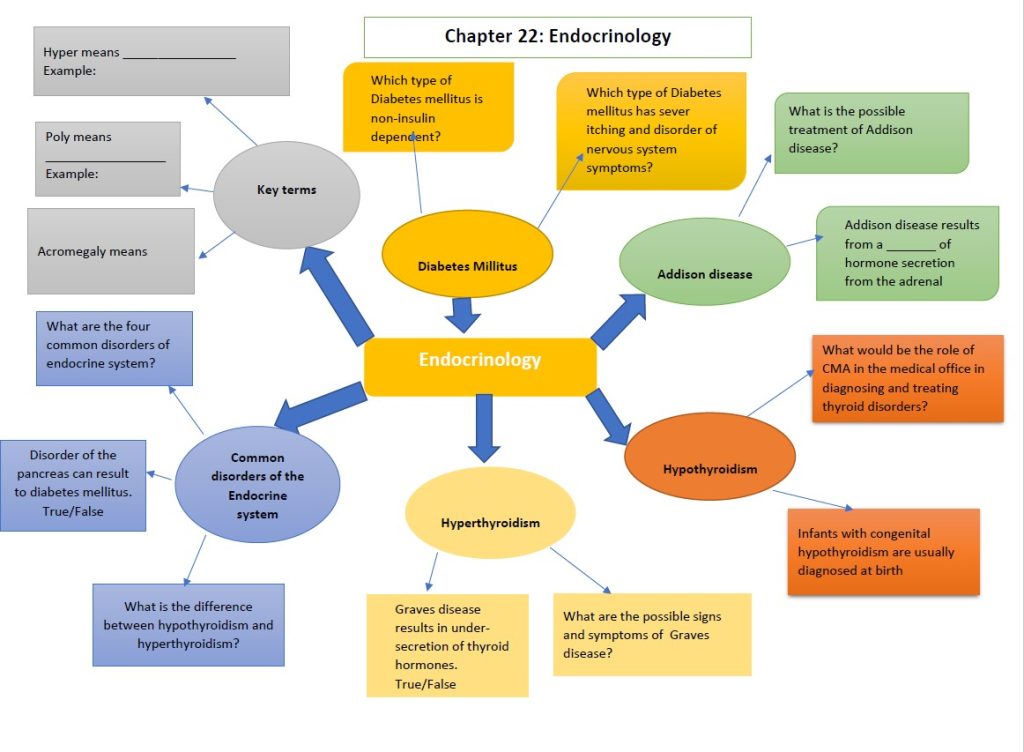
Part 5: Wrap-Up: Set a Personal Goal
Reflect on the lesson and answer the following questions:
- Which active reading strategy do you find most helpful (highlighting or summarizing)? Why?
- Which note-taking method worked best for you? Why?
- What personal goal will you set for applying these techniques in your studies?
- (Example: “I will highlight key points in every chapter I read and create a summary for each section to prepare for weekly quizzes.”)
Media Attributions
- Chapter 22 Mind map

